Introduction to Kale’s Antioxidant Properties
Kale, a leafy green vegetable, is often hailed as a superfood due to its impressive nutrient profile, particularly its Kale’s antioxidant properties. Antioxidants are compounds that combat free radicals, unstable molecules linked to aging and diseases like cancer and heart disease. This article explores how kale’s antioxidants work, common myths, and practical ways to include it in your diet. Comprehensive Analysis of Kale’s Antioxidant Properties
Mechanisms and Benefits
Kale contains antioxidants such as vitamin C, beta-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin, quercetin, kaempferol, and glucosinolates. These compounds neutralise free radicals, reduce inflammation, support eye health, and boost immune function. Studies, like those from Healthline, suggest these properties may lower chronic disease risk, making kale a dietary powerhouse.
Practical Tips for Consumption
To maximise kale antioxidant properties, eat it raw or lightly cooked to preserve heat-sensitive nutrients. Pairing with healthy fats, like olive oil, enhances absorption of fat-soluble antioxidants. Store kale in a cool, dry place to maintain its nutrient content, ensuring you reap the benefits in salads, smoothies, or stir-fries.
Comprehensive Analysis of Kale’s Antioxidant Properties
This detailed analysis delves into the antioxidant properties of kale, a cruciferous vegetable renowned for its health benefits. The content is structured to provide a thorough understanding, optimized for search engines, and written for readability, with evidence from peer-reviewed studies and practical insights.
Kale has been a dietary staple since ancient times and is often referred to as a superfood today. But what drives its health reputation? Consider this: one cup of raw kale (approximately 67 grams) can provide significant antioxidants, potentially offering more vitamin C than some citrus fruits and substantial beta-carotene for eye health. This article explores a comprehensive analysis of kale’s antioxidant properties, mechanisms, common myths, and how to incorporate kale into your diet for optimal benefits, as of April 7, 2025.
What Are Antioxidants and Why Do They Matter?
, supported by research from Medical News Today, makes it a key player in preventive health

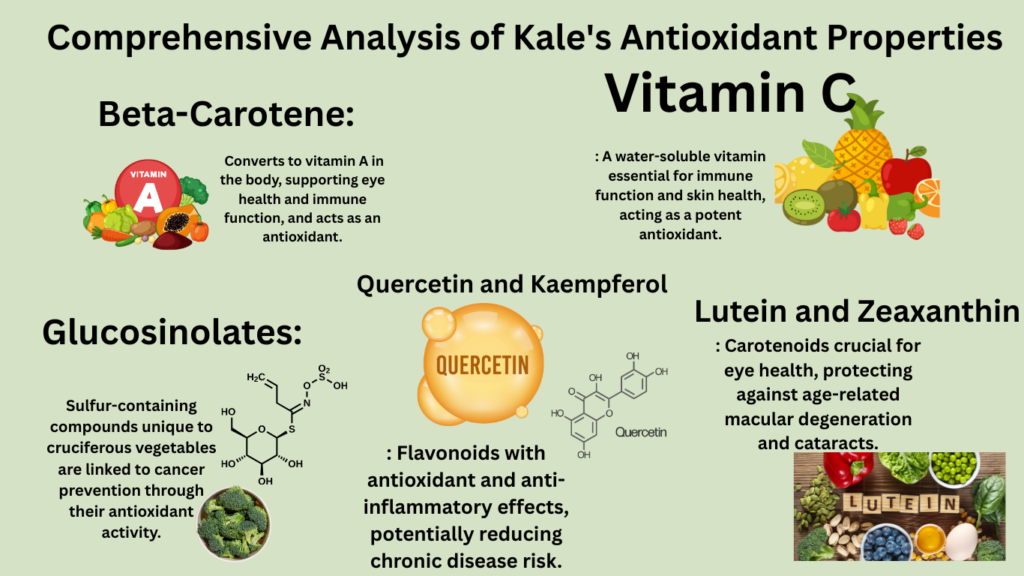
Antioxidants Found in Kale
Kale is packed with a variety of antioxidants, each contributing to its health benefits:
- Vitamin C: A water-soluble vitamin essential for immune function and skin health, acting as a potent antioxidant.
- Beta-Carotene: Converts to vitamin A in the body, supporting eye health and immune function, and acts as an antioxidant.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Carotenoids crucial for eye health, protecting against age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
- Quercetin and Kaempferol: Flavonoids with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, potentially reducing chronic disease risk.
- Glucosinolates: Sulfur-containing compounds unique to cruciferous vegetables, linked to cancer prevention through their antioxidant activity.
According to USDA nutritional data from NutritionValue, one cup of raw kale (67 grams) provides about 22% of the Daily Value (DV) for vitamin C and significant beta-carotene, reinforcing its antioxidant richness.
Mechanisms of Action: How Kale’s Antioxidants Work
The antioxidants in kale operate through several mechanisms to promote health:
- Neutralising Free Radicals: Antioxidants like vitamin C and beta-carotene combat oxidative stress by neutralising free radicals, preventing cellular damage linked to aging and disease.
- Reducing Inflammation: Quercetin and kaempferol have anti-inflammatory properties, potentially lowering the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease and arthritis, as noted in studies from Healthline.
- Supporting Eye Health: Lutein and zeaxanthin, concentrated in the retina, filter harmful blue light, reducing the risk of age-related eye disorders, supported by research from Verywell Health.
- Boosting Immune Function: Vitamin C enhances white blood cell production, while beta-carotene supports immune response, aiding infection prevention.
These mechanisms highlight why kale antioxidant properties are crucial for overall wellness, backed by a review on kale’s phytochemicals from PMC.
Common Myths About Kale’s Antioxidant Properties
Despite its popularity, several myths surround kale’s antioxidants. Below is a table debunking these misconceptions:
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Cooking destroys all antioxidants in kale. | While some heat-sensitive antioxidants like vitamin C may reduce, carotenoids like beta-carotene become more bioavailable when cooked. |
| Kale has more antioxidants than any other vegetable. | Kale is rich, but spinach, broccoli, and others also offer significant antioxidant content, as per WebMD. |
| Antioxidant supplements are as effective as kale. | Whole foods provide synergistic nutrients; supplements may not replicate these benefits, according to BBC Good Food. |
These facts clarify the nuanced role of kale in a balanced diet, addressing common misunderstandings.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Kale
To maximize the kale antioxidant properties, consider these strategies:
- Eat Raw or Lightly Cooked: Consuming kale in salads or lightly steamed helps preserve heat-sensitive antioxidants like vitamin C.
- Pair with Healthy Fats: Adding olive oil or avocado enhances absorption of fat-soluble antioxidants like beta-carotene and lutein, as suggested by Mayo Clinic.
- Store Properly: Keep kale refrigerated in a perforated bag to maintain its nutrient content, ensuring freshness for smoothies, soups, or side dishes.
These tips make it easy to enjoy kale’s benefits daily, aligning with dietary recommendations from SNAP-Ed.
Q&A Section: Addressing Common Queries
Here are answers to frequent questions about kale antioxidant properties, keeping responses clear and concise:
- What are the best ways to cook kale to preserve its antioxidants?
Lightly steaming or stir-frying with a little oil can help preserve many of its antioxidants while making them more palatable. - Can I get enough antioxidants from kale alone?
While kale is rich in antioxidants, it’s best to consume a variety of fruits and vegetables to get a broad spectrum of these beneficial compounds. - Is there a risk of overconsuming antioxidants from kale?
Generally, no, as the body excretes excess water-soluble antioxidants like vitamin C. However, moderation is key, especially for those with certain health conditions. - How does kale compare to other leafy greens in terms of antioxidant content?
Kale is among the top leafy greens for antioxidant content, but others like spinach and Swiss chard also offer significant amounts, as per Verywell Fit. - Does cooking kale reduce its antioxidant properties?
Some antioxidants, like vitamin C, may decrease with cooking, but carotenoids like beta-carotene can become more bioavailable, enhancing absorption. - Can children benefit from kale’s antioxidants?
Yes, kale’s antioxidants support immune and eye health, making it suitable for children when prepared appropriately, such as in smoothies. - Are there any side effects of eating too much kale?
Excessive intake may interfere with thyroid function due to goitrogens, so balance is important, especially for those with thyroid issues.
These answers provide practical guidance, integrating the keyword naturally.
Conclusion: Summarizing Key Takeaways
In conclusion, the kale antioxidant properties make it a valuable addition to any diet. Research suggests its antioxidants, including vitamin C, beta-carotene, and flavonoids, help reduce inflammation, support eye health, and lower chronic disease risk. While cooking methods may affect nutrient levels, eating kale raw or lightly cooked, paired with healthy fats, maximizes benefits. The evidence leans toward kale being a dietary ally, but it’s wise to include a variety of antioxidant-rich foods. Why not try adding kale to your next meal? Whether in salads, soups, or smoothies, it can boost your well-being, leveraging its potent antioxidant profile.


